There are many types of Diagnostic Imaging procedures performed here at SJGHEL.
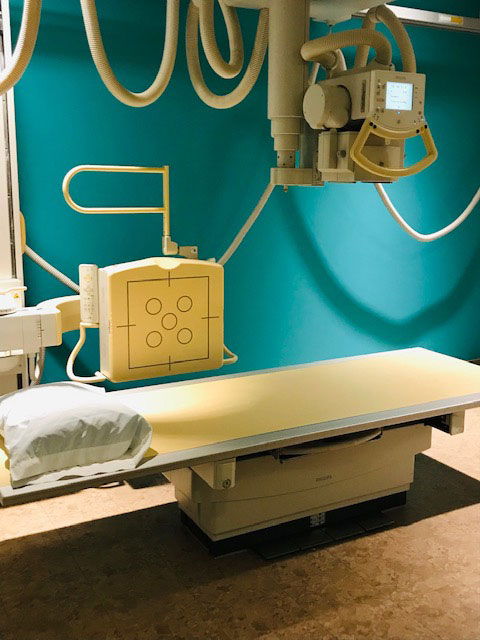
An X-ray is a painless test that uses radiation to produce images of the structures inside your body — particularly your bones. The X-ray beam passes through your body to a digital detector to form an image. This beam is absorbed in different amounts depending on the density of the material it passes through. Dense materials, such as bone and metal, show up as white on X-rays. The air in your lungs shows up as black. Fat and muscle appear as shades of gray.
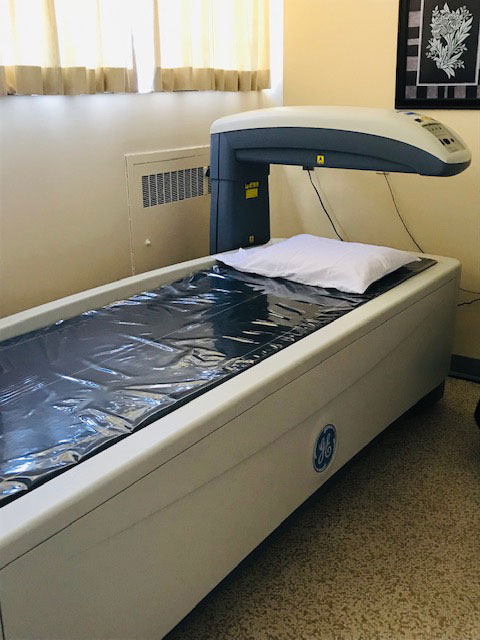
A BMD is painless and quick low dose X-Ray that estimates how dense or thick your bones are. If low bone density is identified (osteoporosis), treatments are available that would aid in the prevention of fractures.
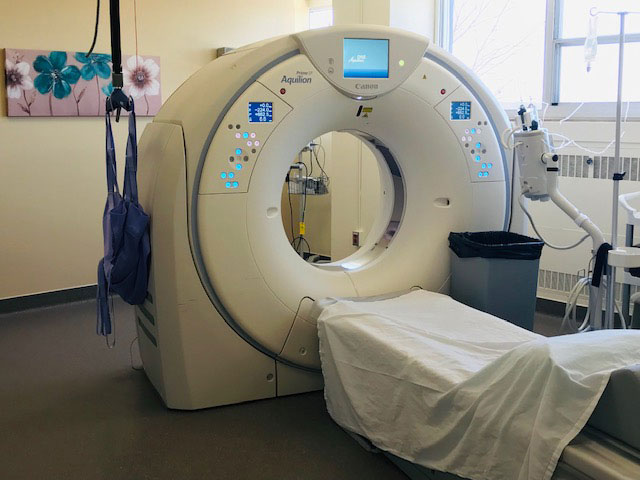
A CT scan can sometimes be required to detect many conditions that are not seen with conventional x-rays. It uses a narrow X-ray beam that circles around your body as the table moves you through the scanner. This creates multiple cross sectional images. Some CT scans require the use of a contrast media in the form of a drink and/or an IV injection. You may be in the department for up to 2 hours depending on the body part being imaged. The contrast media helps to outline blood vessels and organs so they can be more easily seen.
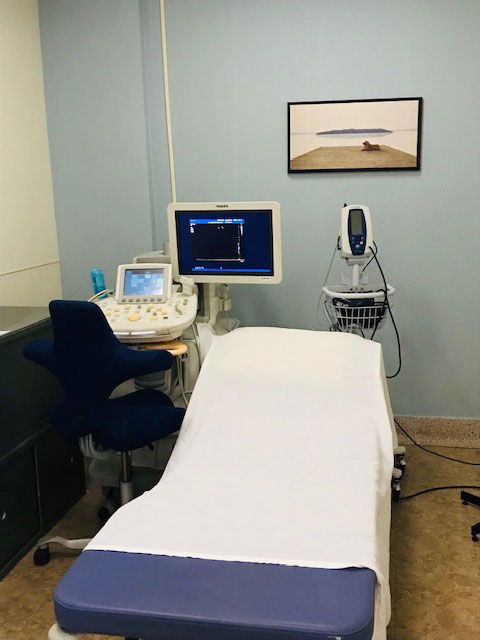
Diagnostic ultrasound is an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. Gel is put on the skin and a transducer is moved over the areas of interest. Depending on the type of ultrasound, you may be asked to drink plenty of water or you may be asked to not drink or eat anything prior to your exam.
An echocardiogram (echo) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of your heart valves, chambers, walls and blood vessels. Gel will be placed on your chest in different locations and a transducer will be moved around on your chest area to obtain the pictures required.